In my “Fundamentals / Roots” series, I describe the underlying theories that impact my understanding of Embodied Leadership & Transformation. This time I a want to speak about Gestalt Theory.
Gestalt, a term derived from the German word for “shape” or “form,” represents a holistic approach to understanding human experience and behavior. In the context of organizations, Gestalt principles emphasize the importance of perceiving the whole rather than merely the sum of its parts. This perspective has profound implications for leadership, team dynamics, and organizational culture. By fostering awareness of the interconnectedness of individuals and their environments, Gestalt has transformed how organizations operate and thrive in complex settings.
The Foundations of Gestalt Theory
Gestalt theory originated in the early 20th century, primarily through the work of psychologists such as Max Wertheimer, Wolfgang Köhler, and Kurt Koffka. This psychological framework posits that individuals perceive objects and experiences as organized wholes rather than isolated components. The core tenets of Gestalt theory can be applied to various fields, including psychology, education, and organizational development.
Key Principles of Gestalt
Understanding the key principles of Gestalt is essential for leaders and organizations seeking to implement this approach effectively. The following principles are foundational:
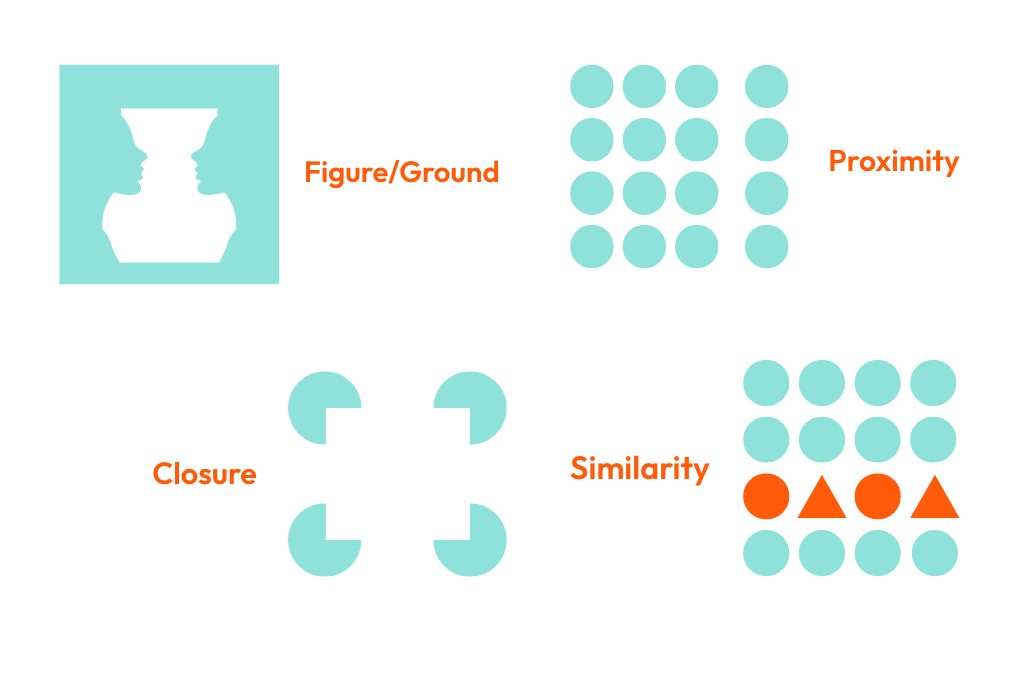
- Figure-Ground Relationship: This principle highlights how individuals focus on specific elements (the figure) while perceiving others as background. In organizations, this can translate to prioritizing key objectives while remaining aware of the broader context.
- Closure: Humans have a tendency to perceive incomplete shapes as complete. This principle encourages leaders to foster environments where team members feel empowered to fill in gaps and contribute to collective goals.
- Proximity: Elements that are close together are perceived as related. In organizational settings, this principle underscores the importance of collaboration and communication among team members.
- Similarity: Similar elements are grouped together in perception. This principle can guide leaders in creating cohesive teams that share common values and objectives.
Gestalt in Organizational Contexts
Applying Gestalt principles within organizations can lead to enhanced communication, improved relationships, and a more cohesive culture. By recognizing the interconnectedness of individuals and their roles, organizations can foster a sense of belonging and purpose among team members.
Enhancing Communication
Effective communication is vital for organizational success. Gestalt principles encourage leaders to create environments where open dialogue is valued. This can be achieved through:
- Active Listening: Leaders should practice active listening to understand the perspectives of their team members fully. This fosters trust and encourages open communication.
- Feedback Loops: Establishing regular feedback mechanisms allows for continuous improvement and alignment with organizational goals.
- Clarity of Purpose: Clearly articulating the organization’s vision and objectives helps team members understand their roles within the larger context.
Building Stronger Relationships
Gestalt emphasizes the importance of relationships in organizational settings. By fostering a culture of collaboration and support, organizations can enhance team dynamics. Key strategies include:
- Team-Building Activities: Engaging in team-building exercises can strengthen relationships and improve collaboration among team members.
- Conflict Resolution: Addressing conflicts promptly and constructively can prevent misunderstandings and promote a positive work environment.
- Shared Goals: Encouraging teams to set and pursue shared goals fosters a sense of unity and collective purpose.
The Impact of Gestalt on Leadership
Leaders who embrace Gestalt principles are better equipped to navigate the complexities of modern organizations. By cultivating self-awareness and emotional intelligence, they can inspire and engage their teams more effectively.
Self-Awareness and Emotional Intelligence
Gestalt encourages leaders to develop a deep understanding of their own emotions and behaviors. This self-awareness is crucial for effective leadership, as it allows leaders to:
- Recognize Personal Triggers: Understanding what influences their reactions enables leaders to respond thoughtfully rather than react impulsively.
- Model Vulnerability: Leaders who demonstrate vulnerability create a safe space for team members to express their thoughts and feelings.
- Foster Empathy: By being attuned to their own emotions, leaders can better empathize with the experiences of their team members.
Creating a Culture of Trust
Trust is a cornerstone of effective leadership. Gestalt principles can help leaders cultivate a culture of trust within their organizations. Strategies include:
- Transparency: Openly sharing information and decision-making processes fosters trust and accountability.
- Consistency: Consistent behavior and communication from leaders build credibility and reliability.
- Empowerment: Encouraging team members to take ownership of their work fosters a sense of trust and autonomy.
Gestalt Practices in Organizational Development
Implementing Gestalt practices within organizational development can lead to transformative change. By focusing on the whole system, organizations can create environments that support growth and innovation.
Holistic Approaches to Change
Gestalt encourages organizations to adopt holistic approaches to change management. This involves considering the entire system rather than isolated components. Key practices include:
- Systemic Thinking: Leaders should consider how changes in one area of the organization impact other areas, fostering a comprehensive understanding of organizational dynamics.
- Participatory Processes: Involving team members in decision-making processes enhances buy-in and commitment to change initiatives.
- Continuous Learning: Organizations should cultivate a culture of continuous learning, encouraging experimentation and adaptation.
Measuring Impact and Success
To assess the effectiveness of Gestalt practices, organizations must establish metrics for success. This can include:
- Employee Engagement Surveys: Regularly measuring employee engagement can provide insights into the effectiveness of Gestalt practices.
- Performance Metrics: Tracking performance indicators can help organizations evaluate the impact of holistic approaches on productivity and outcomes.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implementing feedback loops allows organizations to continuously refine their practices based on team input.
Conclusion
Gestalt offers a powerful framework for understanding and enhancing organizational dynamics. By embracing the principles of Gestalt, leaders can foster a culture of collaboration, trust, and continuous improvement. The holistic approach encourages organizations to view challenges as interconnected, leading to more effective solutions and a thriving workplace. As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of the modern world, the principles of Gestalt will remain a vital resource for fostering resilience and adaptability.
Embrace Gestalt Principles with Julius
Ready to integrate Gestalt principles into your organization? I am happy to guide you through this journey with leadership development, business coaching or change & transformation consulting. Learn More about how I can support your personal and professional growth, and help you and your company achieve your goals in a more effective and vibrant way.